Provisioning Kubernetes with SemaphoreUI and Kubespray: Automating Cluster Deployment
Semaphore UI is an open-source web-based interface for managing and automating Ansible tasks and CI/CD workflows. It allows DevOps engineers to visually organize playbooks, run commands, and monitor automation pipelines without complex terminal operations. This makes it a powerful tool for simplifying infrastructure deployment, especially when combined with Kubespray, an Ansible-based Kubernetes installer.
In this article, we’ll walk you through how to install and deploy Kubernetes using SemaphoreUI and Kubespray — from setting up your inventory and playbooks to running automated tasks via Semaphore pipelines. This approach not only reduces manual effort but also ensures repeatable, consistent, and production-ready Kubernetes deployments suitable for DevOps teams and cloud-native environments.
Topology
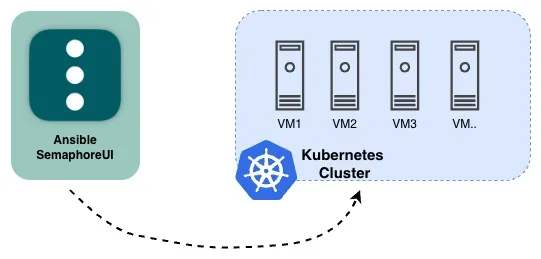
Lab Details
Kubernetes Version: v1.31.9
ETCD : Kubeadm
CNI: Calico
CRI: Containerd
OS: Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS
| IP | Hostname |
|---|---|
| 10.10.61.21 | k8s-master-01 |
| 10.10.61.22 | k8s-master-02 |
| 10.10.61.23 | k8s-master-03 |
| 10.10.61.25 | k8s-worker-01 |
| 10.10.61.26 | k8s-worker-02 |
Prerequisites
- SemaphoreUI installed
- All Kubernetes nodes can connect to each other via passwordless SSH
Preparation
- Go to the terminal where
SemaphoreUIis located, then clone kubespray. This lab uses Docker
docker exec -it semaphore-semaphore-1 sh
git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray /tmp/kubespray
cd /tmp/kubespray- Then switch to the
release-2.27branch and installrequirements.txt
/tmp/kubespray $ git checkout release-2.27
/tmp/kubespray $ pip install -U -r requirements.txtDeploy Steps
- The first step is to create a project in the Semaphore UI.
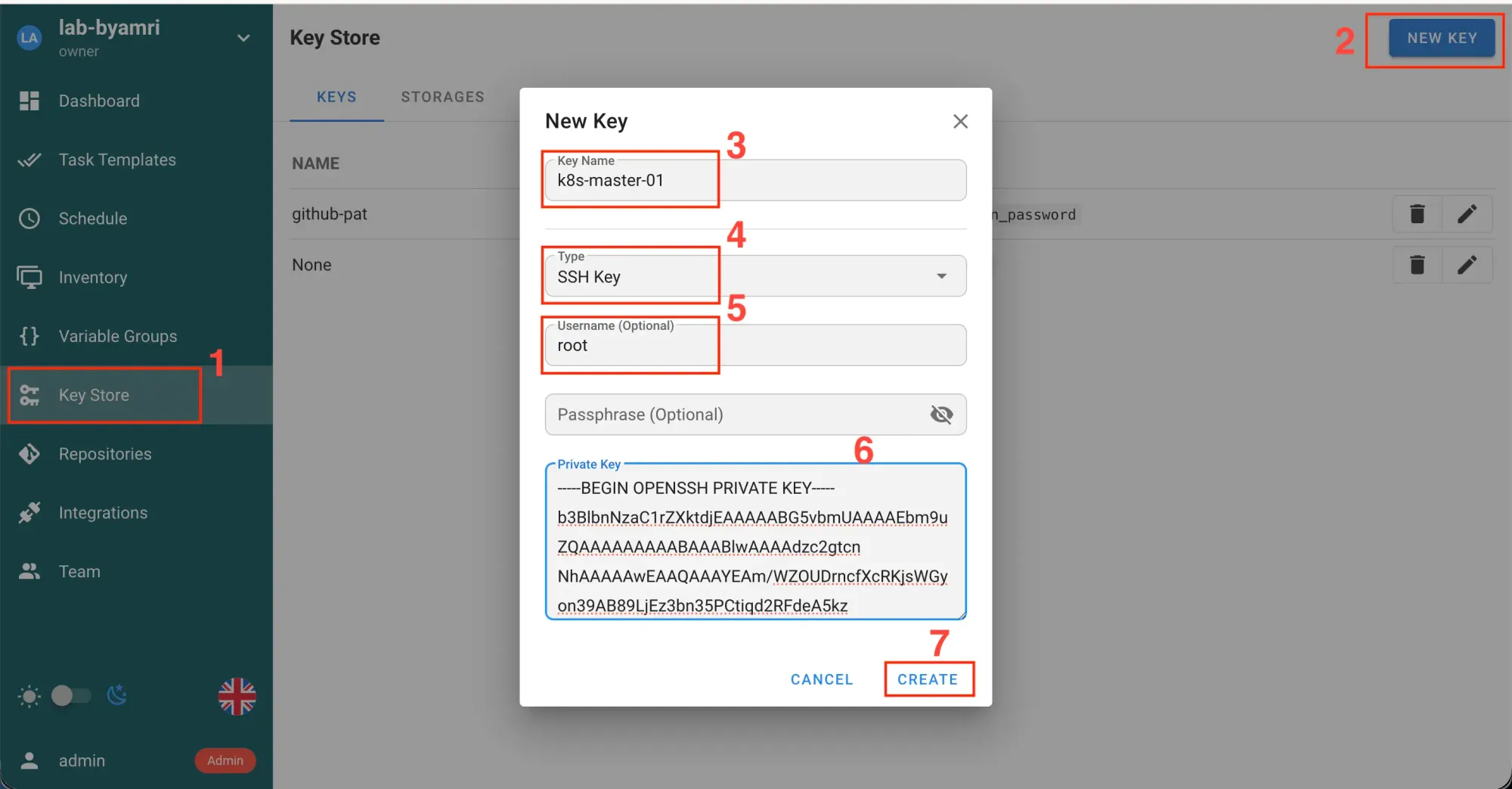
- Then, copy the
PrivateKeyfromk8s-master-01as a jumphost for SSH to all nodes.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa
...
-----BEGIN OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
...
...
...
-----END OPENSSH PRIVATE KEY-----
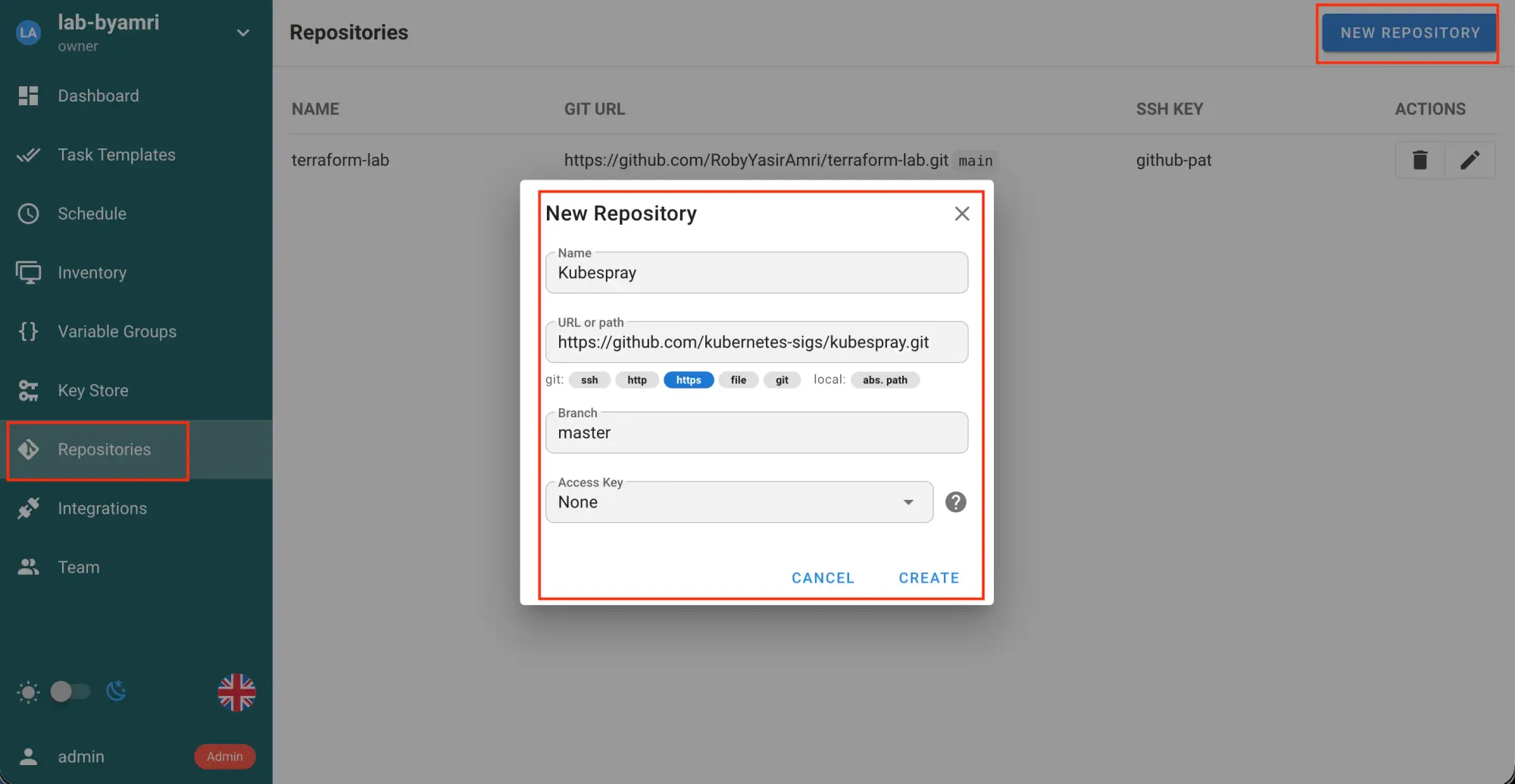
- Then, create a repository.
Click Repository → NEW REPOSITORY-> SAVE
- Create
Inventoryto include all hosts
Click Inventory → Ansible Inventory → NEW INVENTORY → Create
all:
hosts:
k8s-master-01:
ansible_host: 10.10.61.21
ip: 10.10.61.21
access_ip: 10.10.61.21
short_hostname: master-01
node_taints:
- "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane=:NoSchedule"
k8s-master-02:
ansible_host: 10.10.61.22
ip: 10.10.61.22
access_ip: 10.10.61.22
short_hostname: master-02
node_taints:
- "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane=:NoSchedule"
k8s-master-03:
ansible_host: 10.10.61.23
ip: 10.10.61.23
access_ip: 10.10.61.23
short_hostname: master-03
node_taints:
- "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane=:NoSchedule"
k8s-worker-01:
ansible_host: 10.10.61.25
ip: 10.10.61.25
access_ip: 10.10.61.25
short_hostname: worker-01
node_labels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""
type: "app"
k8s-worker-02:
ansible_host: 10.10.61.26
ip: 10.10.61.26
access_ip: 10.10.61.26
short_hostname: worker-02
node_labels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""
type: "app"
children:
kube_control_plane:
hosts:
k8s-master-01:
k8s-master-02:
k8s-master-03:
kube_node:
hosts:
k8s-master-01:
k8s-master-02:
k8s-master-03:
k8s-worker-01:
k8s-worker-02:
etcd:
hosts:
k8s-master-01:
k8s-master-02:
k8s-master-03:
k8s_cluster:
children:
kube_control_plane:
kube_node:
calico_rr:
hosts: {}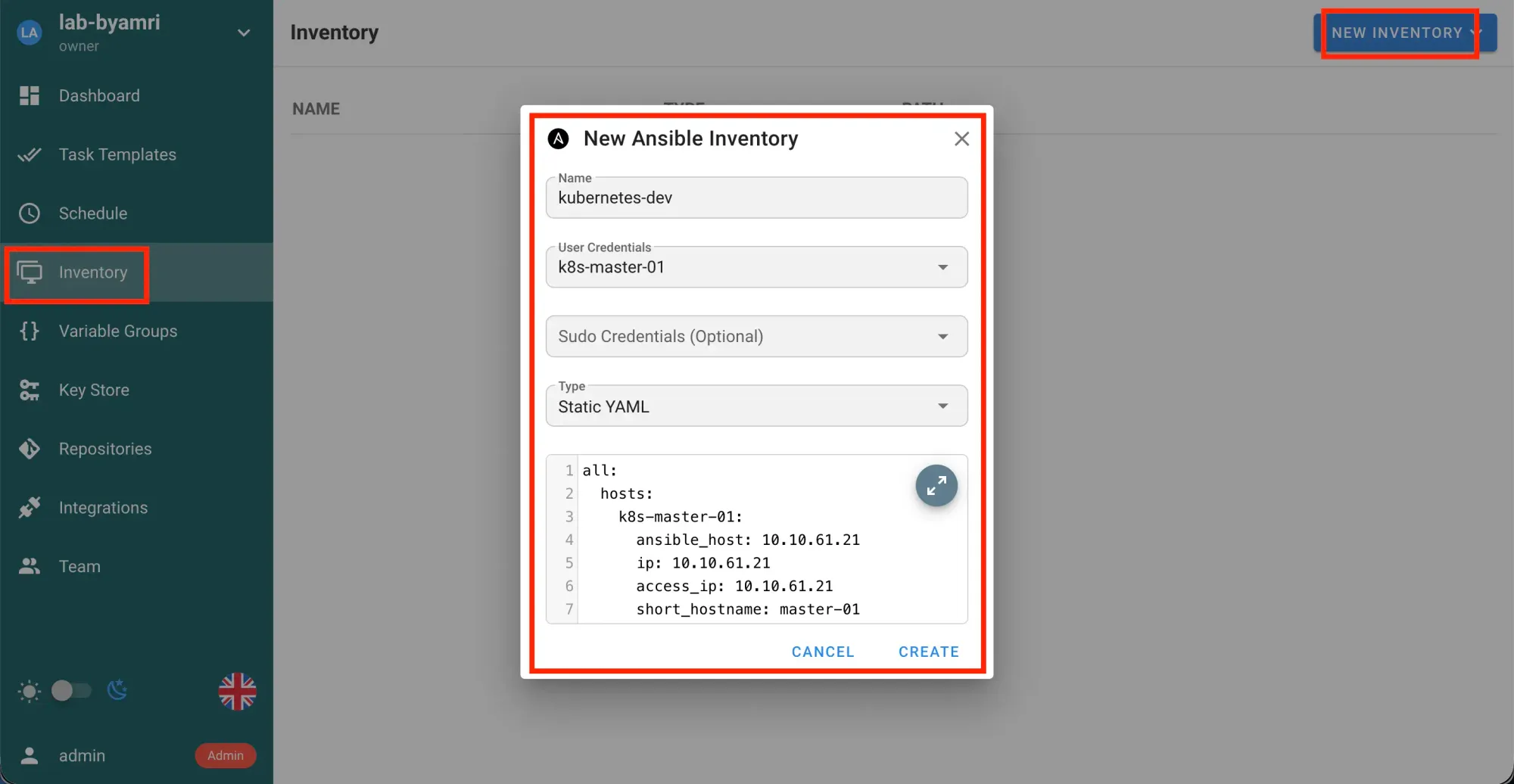
- Then create
Environmentto define the cluster version, name clusters, etc.
Click Variable Groups → NEW GROUP → SAVE
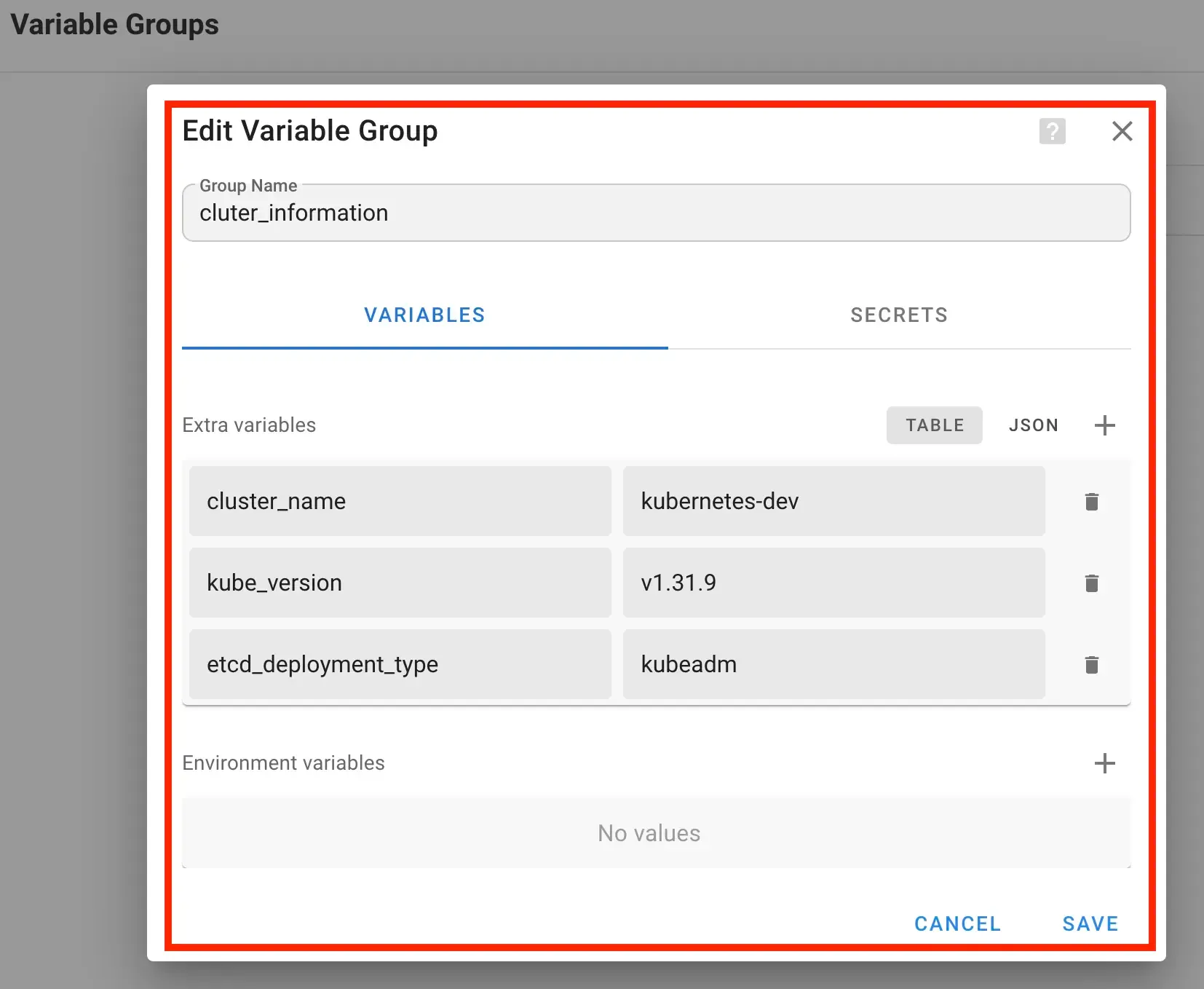
etcd_deployment_type uses kubeadm so that etcd is a static manifest, not systemdSource: https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray/blob/master/docs/operations/etcd.md#kubeadm
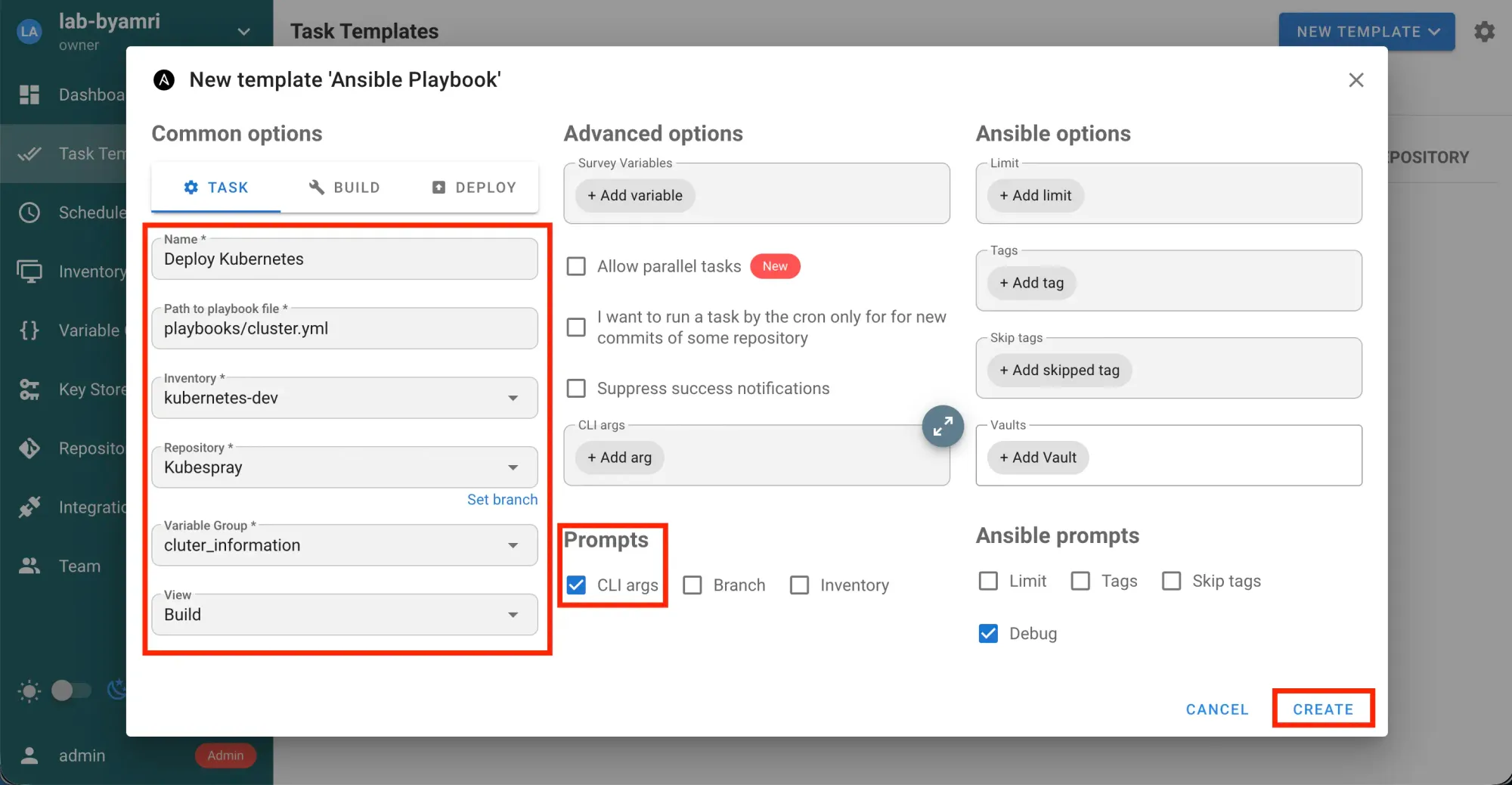
- Create a template:
Task Templates→New Template→Ansible Playbook→ Input Value →Create
Deploy Cluster
- Select
Task Templatesand clickDeploy Kubernetes→RUN
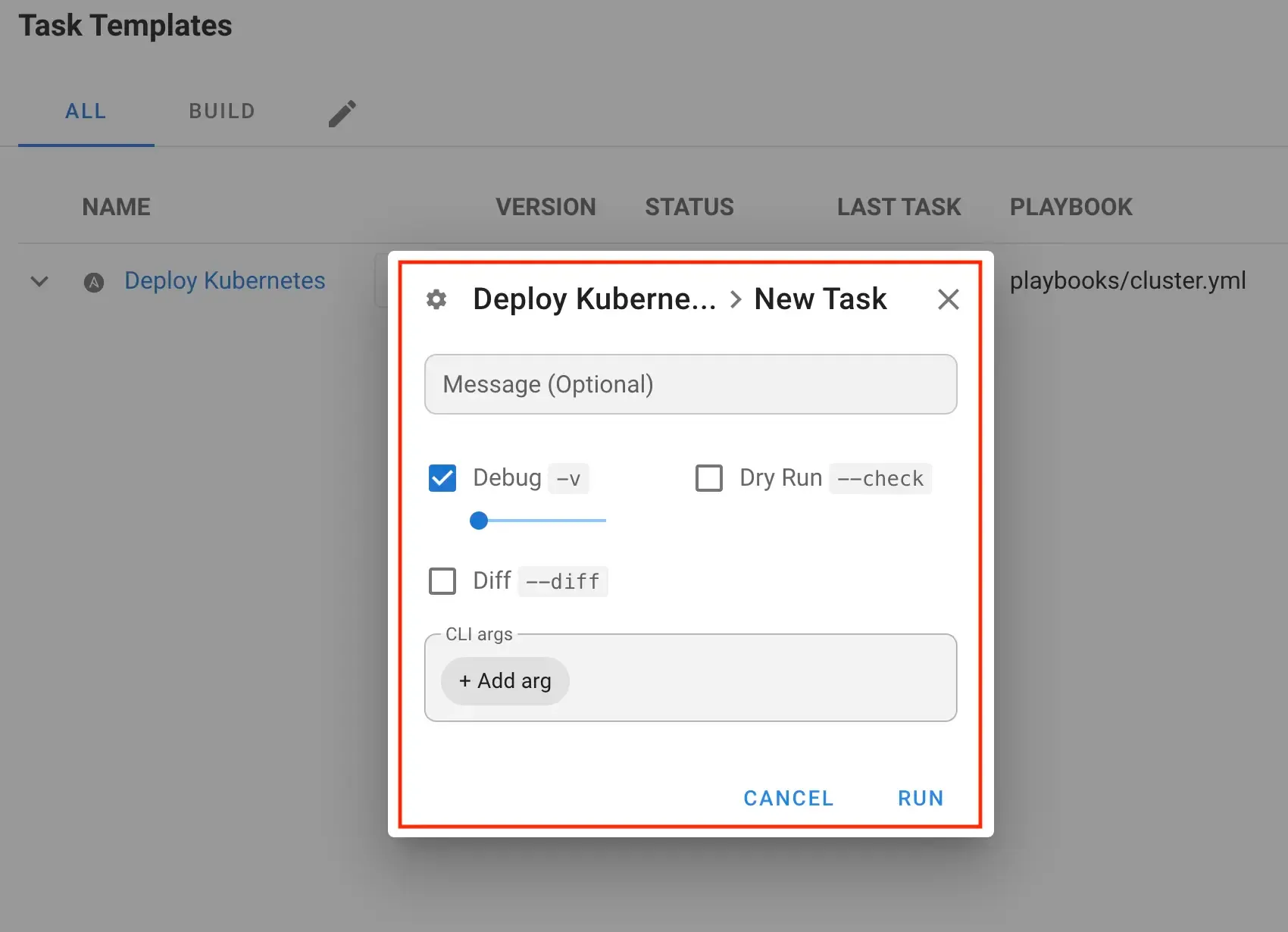
- Wait for the deployment process to complete
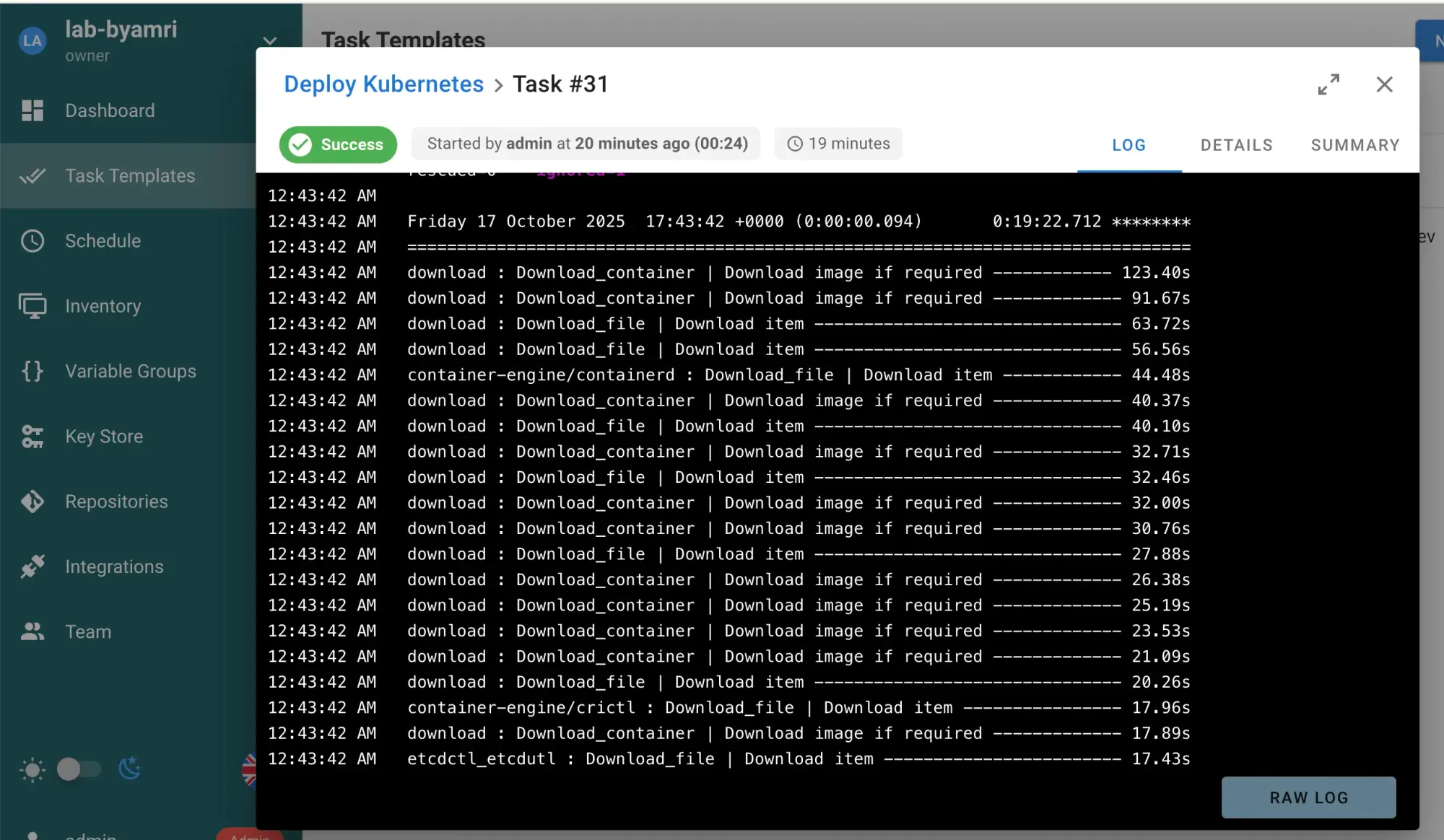
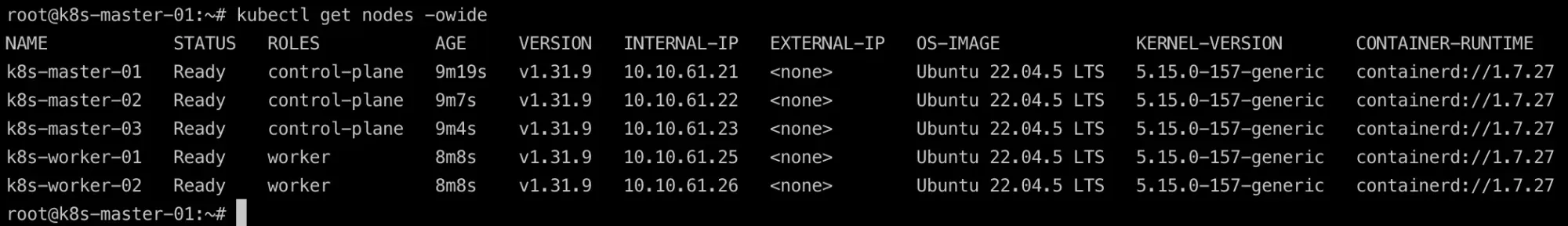
Verification
- Check the node status
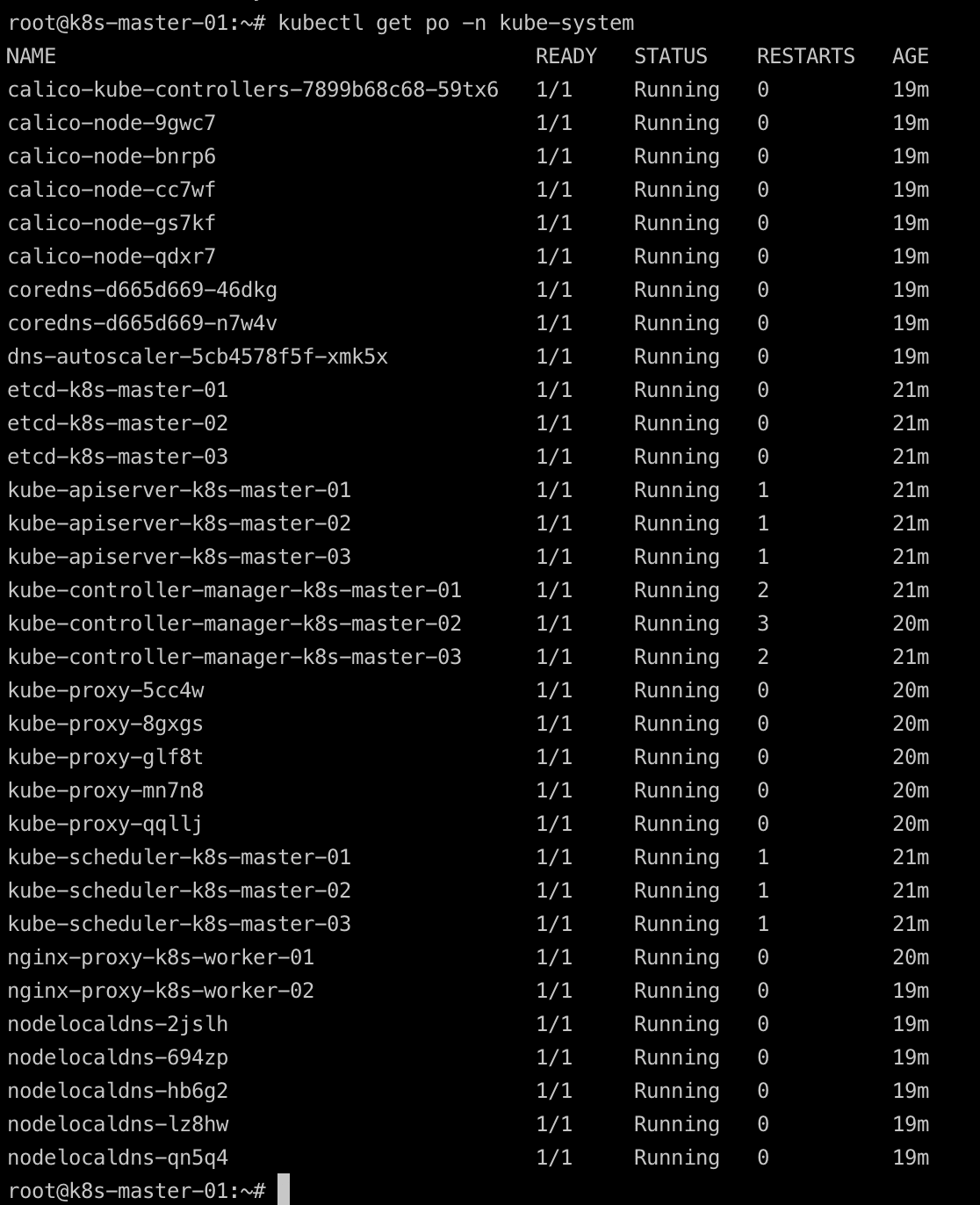
- Check kube-system pods
By combining SemaphoreUI and Kubespray, deploying Kubernetes becomes more efficient, consistent, and less error-prone. This automation-driven approach not only simplifies infrastructure management but also accelerates your CI/CD workflows — helping teams focus more on innovation rather than manual configuration.